Neo4j is a graph database that stores data in a graph. Data is stored as nodes and relationships instead of tables or documents. Graph databases are particularly useful when the connections between data are as important as the data itself
The objects are referred to as nodes (vertices) connected by relationships (edges). Nodes are grouped by or categorized using labels. Labels describe what the nodes are, for example, Person, Company, Location. Nodes of the same type would have the same label. Labels allow you to distinguish between different types of nodes and filter the graph
Nodes can have multiple labels, for example, Michael is a Person and could also be an Employee. Relationships are the lines in the graph. Relationships describe how nodes within the graph are connected to each other.
You can store data against nodes and relationships as Properties. Properties are named key, value pairs; for example firstName, lastName, and position. Nodes and relationships can have any number of properties, and those of the same type do not have to have the same properties (i.e. Neo4j is schemaless). Properties have a type (integer, Boolean, string, list, etc.) and can be unique identifiers (keys) for specific node labels.
Neo4j uses the graph structure to store data and is known as a labeled property graph
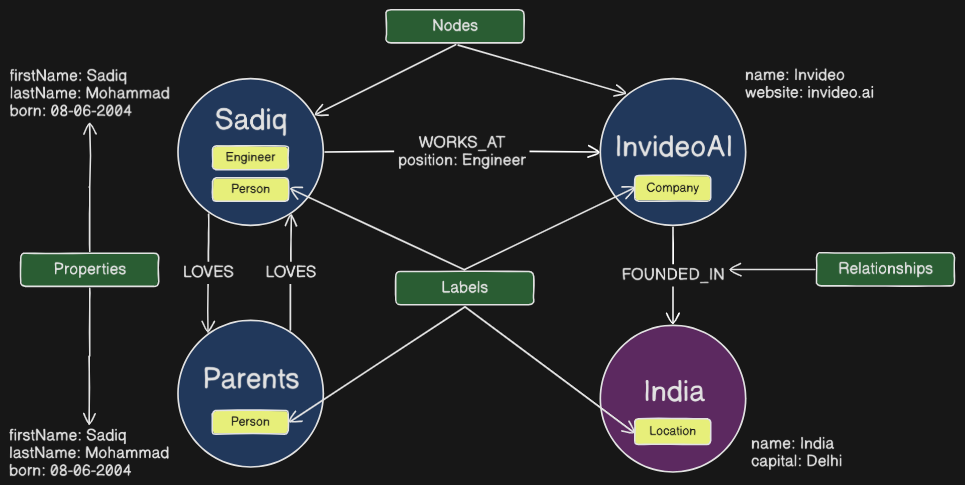 Note: watch the Green boxes for context(not linked to everything, but they are linked)
Note: watch the Green boxes for context(not linked to everything, but they are linked)
Knowledge Graphs & Generative AI
GenAI applications need access to the meaning in data, and knowledge graphs can provide this context. Knowledge graphs provide a structured way to represent entities, their attributes, and their relationships, allowing for a comprehensive and interconnected understanding of the information.