It’s a way to trade financial instruments like stocks and options, using Algorithms and Machines at very high speeds which makes tiny profits per trade, but as they made in high volumes it cumulatively becomes very high profits
They Mainly target these three things:
- Price Difference between exchanges
- Temporary imbalances in the order book
- Slow price updates
And for all of this Speed matters a lot
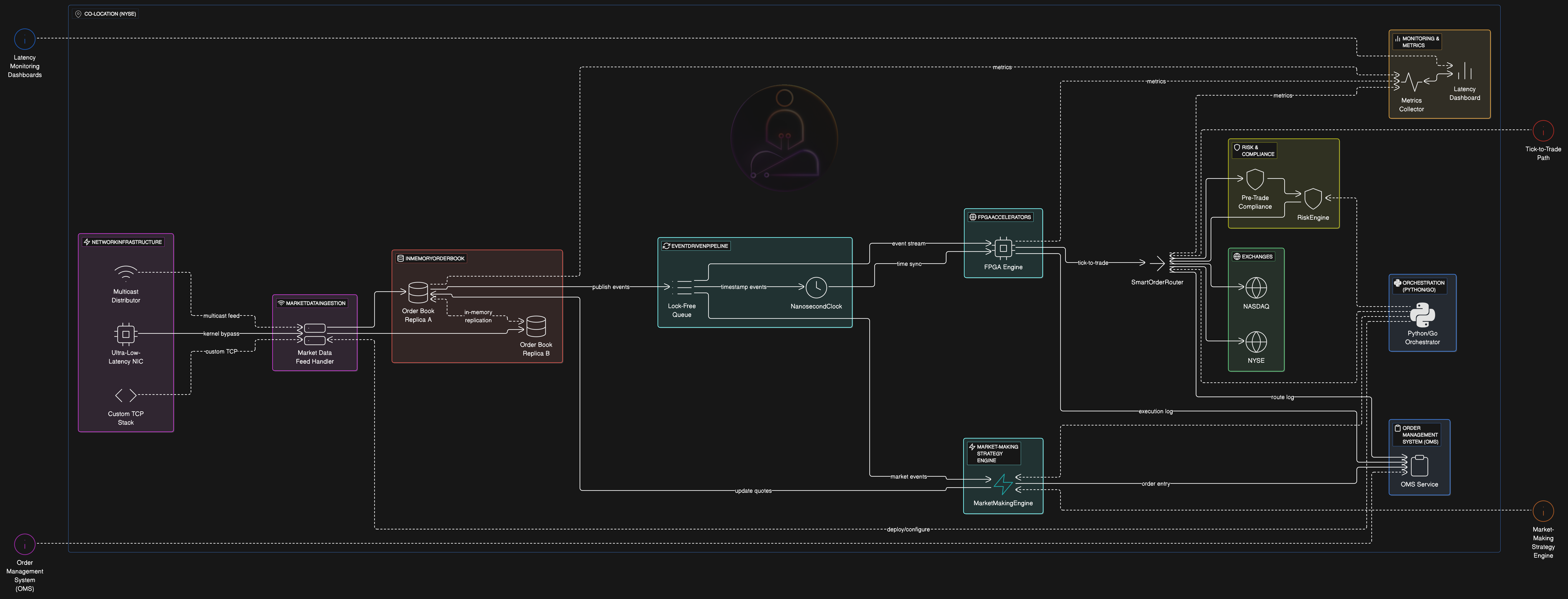
Market data Ingestion
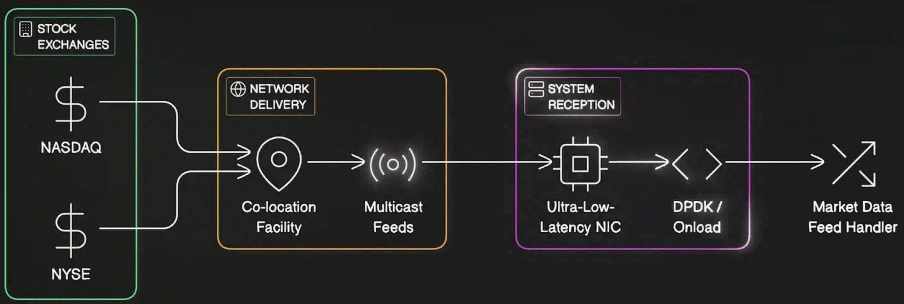 The HFTs pull data from Exchanges which are placed in the same
The HFTs pull data from Exchanges which are placed in the same Co-location Facility near the respective Stock Exchange Servers
These HFTs use Multicast Feeds for data transportation, which is a type of network protocol used for high speed, same data transmission(like same stock ticks for everyone)
This Data is received via a specialized hardware like Ultra Low Latency NIC(Network Interface Card) which is a custom TCP stack, and some time a Kernel Bypass software like DPDK/Solar Onload which later passed on to a Market Data Feed Handler which parses the raw stream, decodes the protocol and transforms data into a format which system can understand
Updating the Order Book
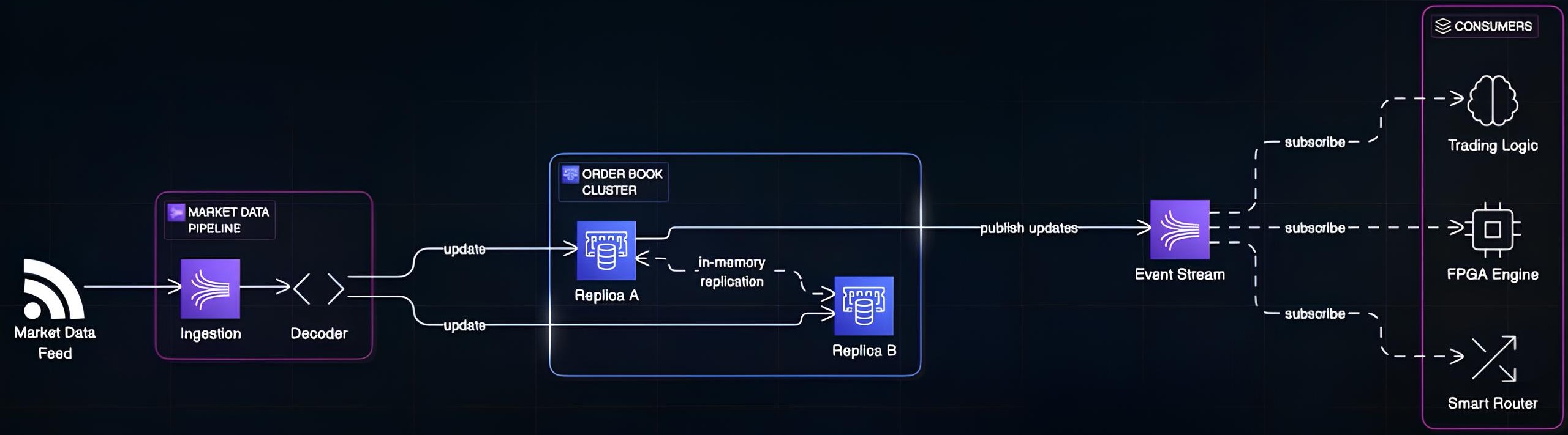 The Order book is the live snapshot for all current buy and sell orders. And this is maintained in In-Memory to avoid any IO or Disc Latency, It’s updated in real-time by every incoming message triggering a precise update and replicate in two shard, which are kept in sync with an In-memory replication to avoid fault tolerance. And these updates are published into a event Stream, by letting the Consumers(Trading Logic, FPGA Engine, Smart Router) to consume further
The Order book is the live snapshot for all current buy and sell orders. And this is maintained in In-Memory to avoid any IO or Disc Latency, It’s updated in real-time by every incoming message triggering a precise update and replicate in two shard, which are kept in sync with an In-memory replication to avoid fault tolerance. And these updates are published into a event Stream, by letting the Consumers(Trading Logic, FPGA Engine, Smart Router) to consume further
Event Driven Pipeline
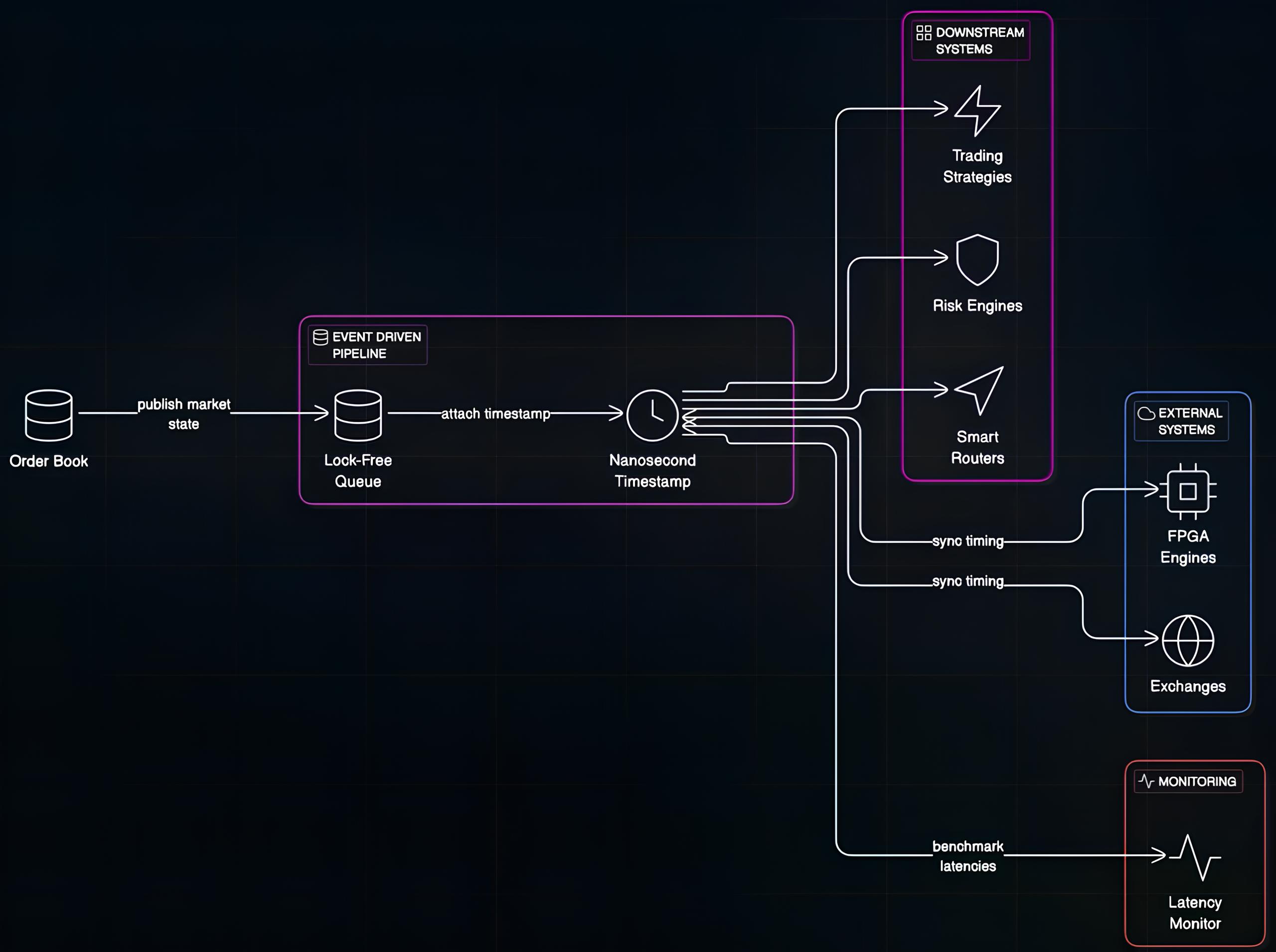 Once the data is updated in Order Book, they are pushed into a Real-time Event driven Pipeline which pushes it into a
Once the data is updated in Order Book, they are pushed into a Real-time Event driven Pipeline which pushes it into a Lock-Free Queue because even a slightest delay caused by locking threads can impact the trades timing and all these events are attached with a Timestamp using a Nanosecond Timestamp precision clock, this level of timing and accuracy allows systems to
- Maintain exact sequence of market updates
- Benchmark internal component latencies
- Sync perfectly with external systems like
FPGA EnginesandExchanges
The result is precise timestamp stream of market events that downstream systems like Trading Strategies, Risk Engines and Smart Routers consume
FPGA 101
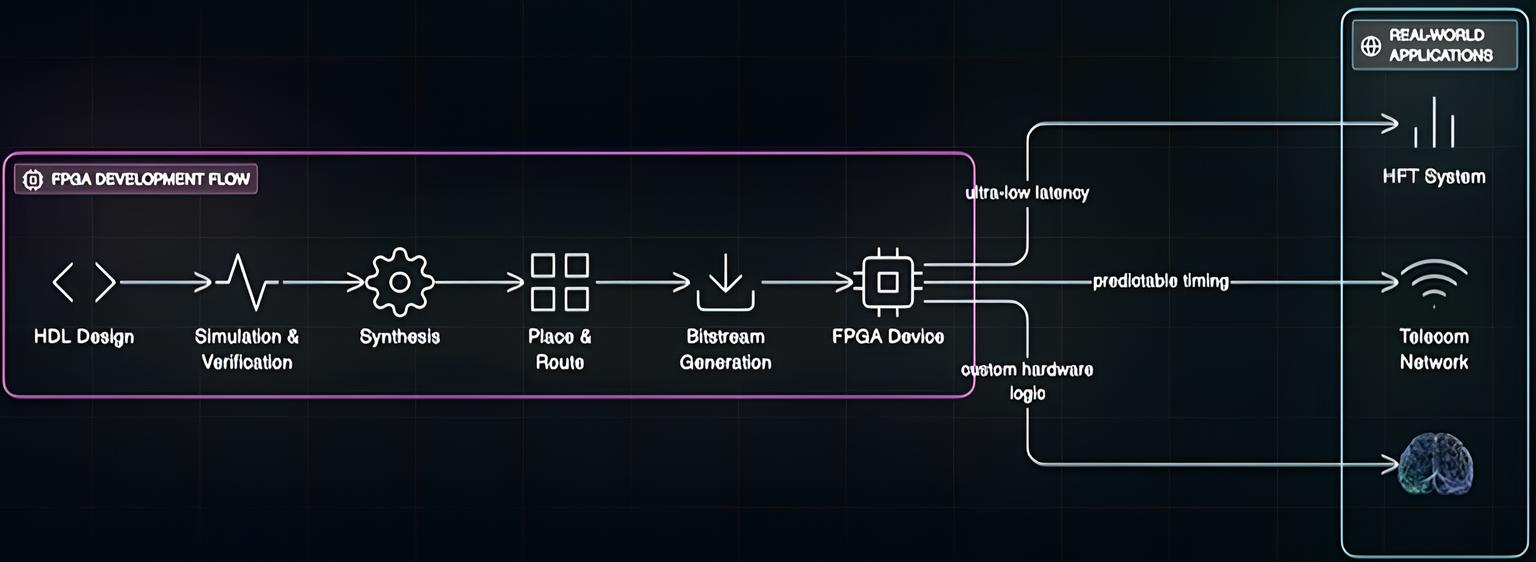
FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array) is a special type of integrated circuit which contains many electronic components like logic gates, memory and connectors. It’s different from CPU and GPU as it’s not locked into one function, like we can reprogram it even after it’s built allowing it to behave like a custom piece of software
- Inside FPGA there are small reusable units called
Configurable Logic Block (CLBs)as shown in figure. - In these CLPBs there is a component called
LUT(Look up table)which is simply an hard-coded if else table which maps inputs to outputs. In this case LUT acts as anXOR Gatewhich can be re-programmed to act like a single function. - Inside FPGA there are wires which connects CLBs with each other called
Programmable Interconnects, this can be configured as we like, giving us ability to decide the dataflow inside the FPGA. - IO blocks are Part of FPGA that connect the chip to the outside world, they sit next to the Input and the Output Pins to setup Send Data, Receive Data or to Stay Ideal, this helps FPGA to talk with external devices like Sensors, Displays and Other Chips
- To Program FPGA we use a Hardware description language(HDL) or STL like Verilog or VSTL. An HDL describes what hardware it should be not what it should do. So when we’re writing code in Verilog or VHDL, we’re not directly saying like put this value in this LUT rather we are defining what logic we want and
FPGA ToolchainlikeVivadoorQuatersfigures out how to implement the logic using that LUT. For Example if we writeassign y = a ^ bin Verilog,- It will recognize that an XOR gate is needed
- It will look at the available LUTs
- And Program one of them to behave like a 2-input XOR gate by setting its truth table accordingly
- To Translate the code into a hardware circuit we use a
Synthesis Toolwhich figures out things like LUTs, Flip-Flops, Routing inside FPGA to match out design- First it takes the Verilog/VHDL code, and generates a
Netlistwhich is a blue print of how logic gates and connections should be laid out in hardware - Later it Compiles to FPGA configuration and generates the
Bitstreamwhich programs the FPGA
- First it takes the Verilog/VHDL code, and generates a
FPGA Acceleration in HFTs
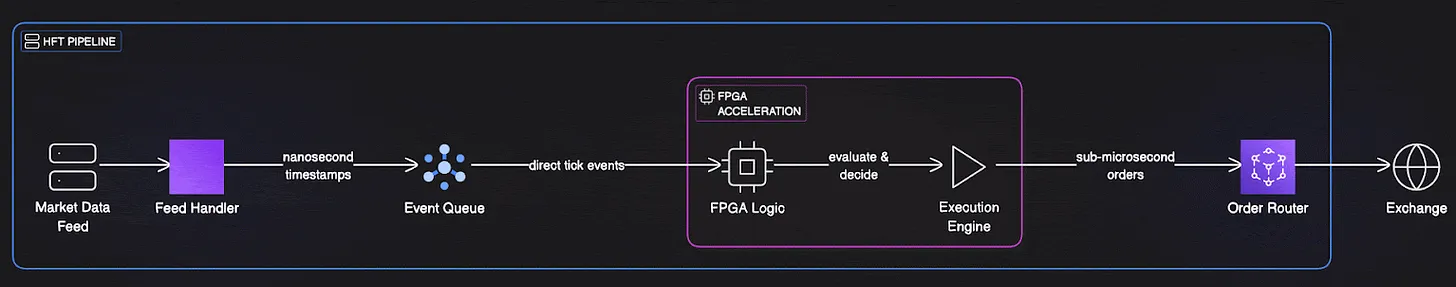
FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array) is a type of reconfigurable chip that can run custom logic at the speed of hardware without overhead of CPU or OS. These are used for Tick-To-Trade Execution, it means when a tick arrives it is evaluated by logic on the FPGA and a trading decision can be made in sub microsecond latency
And also before executing the orders they go into a Order Router which checks with Risk Management Service and decides the best exchange to hit
The Complete System
Earning via Arbitrage Using Microwaves
Arbitrage - Multiple Markets have different values of same stock for a short period of time, where we can make money by buying or selling
For example, If in London Stock Exchange(LSE) let’s take Carnival Corp (CCL) have a value of 1 CCL = 30 Dollars and in US Stock Exchange(NYSE) the price is 1 CCL = 31 Dollars. Here there is an Arbitrage(we can buy a stock in LSE and sell the same stock in NYSE for profit until the price gets corrected(very less time)) and we need to transmit data via high speeds to make profit, The obvious choice is to use optical fiber cables, but for more speed HFTs setup tall antennas to send data via Microwaves but Microwaves are not reliable as they are easily prone to any obstacles and as Earth is round, we need to keep them tall, thus costing us more, for that reason we use fiber optic cables as backup and use microwaves at places where the obstacles are low
Q Why we use Microwaves when they do the same job of fiber optic cables ?
A For Speed. Microwave radio signals travel through the air at a speed close to the speed of light. Fiber optic cables use light pulses to transmit data through glass or plastic fibers. While light travels slower in fiber than in air, but they can carry more data, reliably and less prone to weather and other external factors