Interrupts are mechanisms that allow a program to be temporarily suspended in order to execute another routine known as the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR). When an interrupt occurs, the current program’s state is saved on the stack, which utilizes a Last In, First Out (LIFO) structure to manage nested interrupts effectively.
There are two types of Interrupts:
- Software Interrupts
- To generate an Software Interrupt we use a Instruction called RSTn.
- Hardware Interrupts
- Priority - The Interrupt with Lower priority is preferred when two Interrupts occur together, the other Interrupt is Sent to Pending State
- Trigger - To know a Interrupt came or not the
Interrupt Pinsshould be1. There are two types of Triggers- Edge Triggered - It tells an Interrupt is present only if the pin value moved from
0to1. e.g.: A gun will only shoot bullet when it pulled and triggered ( 0 to 1 - Triggering is necessary irrespective of the pull ) - Level Triggered - It tells an Interrupt is present if the pin value is
1, irrespective of it’s initial state. e.g.: A Machine gun shoots when it is triggered (1 - not care about the pulling )
- Edge Triggered - It tells an Interrupt is present only if the pin value moved from
- Mask by SIM - It is used to stop particular any Interrupt except
TRAPandINTR - Disable by DI - It is used to stop Interrupts except
TRAP - Vector Address - If the address of an
ISRis fixed we call it an Vector Address. OnlyINTRdoesn’t have an fixedISRaddress thus it is slow compared to others as to execute it the processor need to fetch the address
| Interrupt | Priority | Trigger | Mask by SIM | Disable by DI | Vector Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRAP | 1 | E / L | ❌ | ❌ | 0024H |
| RST 7.5 | 2 | E | ✅ | ✅ | 003CH |
| RST 6.5 | 3 | L | ✅ | ✅ | 0034H |
| RST 5.5 | 4 | L | ✅ | ✅ | 002CH |
| INTR | 5 | L | ❌ | ✅ | Non - Vector (Device) |
Interrupt Structure of 8085
 Note: To enable interrupts within an Interrupt Service Routine (ISR), we typically use the EI (Enable Interrupt) instruction. This instruction allows other interrupts to be processed while the current ISR is executing, effectively enabling interrupt priorities and permitting nested interrupts.
Note: To enable interrupts within an Interrupt Service Routine (ISR), we typically use the EI (Enable Interrupt) instruction. This instruction allows other interrupts to be processed while the current ISR is executing, effectively enabling interrupt priorities and permitting nested interrupts.
For an interrupt to execute, the following conditions must be met:
- The interrupt pin should be set to 1 (active).
- The interrupt should be unmasked (enabled).
- Global interrupts must be enabled by executing the EI instruction.
8259 Communication with 8085
- First
8259will send the Interrupt in any of the interrupt pins of8085viaINTR - Then
8085will send theINTA(bar)to8259 - Then
8259will send anOpcodeto8085- If the Opcode have
RSTnthen it will see the address ofISRby doingn x 8and the function calling continues - If the Opcode have
CALL, then it also needs the address then8259will send anINTRand getslower byteof address viaINTA(bar)and again will send anINTRand getshigher byteof address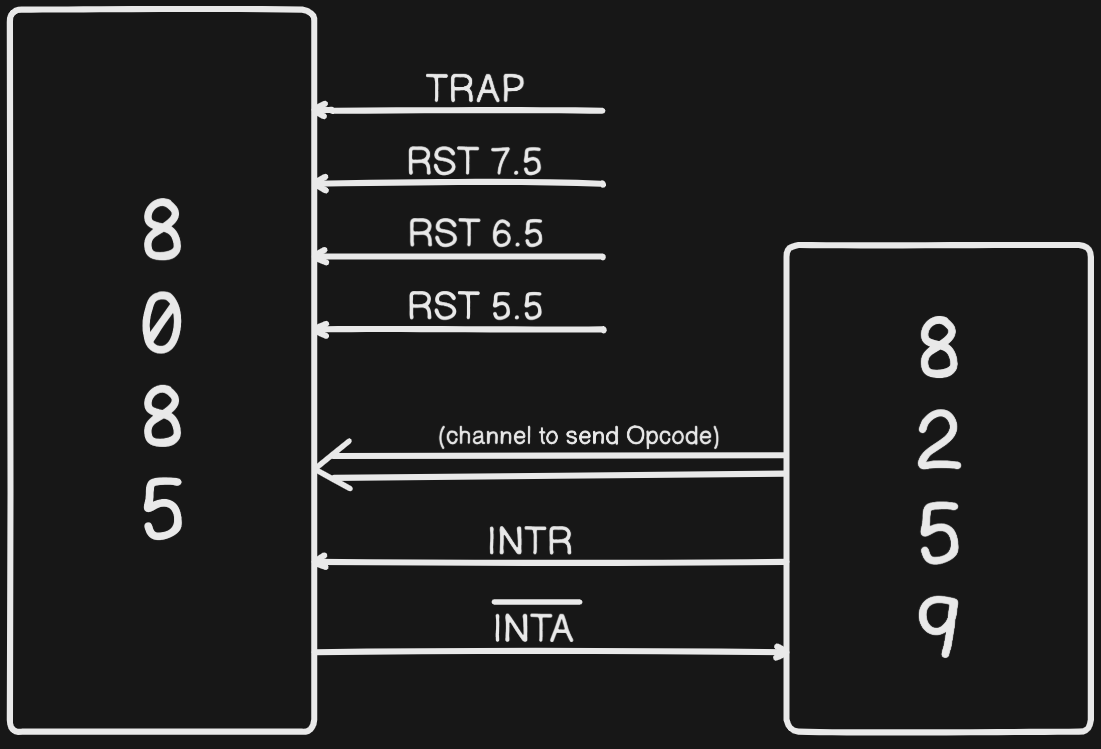
- If the Opcode have